INSTRUMENTS CURRENCY TRADING(Forex).

The World of Currency Trading (Forex)
Currency trading, also known as Forex (Foreign Exchange), is the process of buying and selling currencies with the aim of making a profit. It is one of the most actively traded markets globally, with trillions of dollars being exchanged daily. To be successful in currency trading, it is essential to understand the various instruments involved.
1. Currency Pairs
In Forex, currencies are always traded in pairs. Each pair consists of a base currency and a quote currency. The exchange rate represents the value of one currency relative to another. Popular currency pairs include EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY.
2. Spot Market
The spot market is where currencies are bought and sold for immediate delivery. It is the most common and straightforward method of currency trading. Traders can take advantage of currency fluctuations to make profits. Trades are settled within two business days.
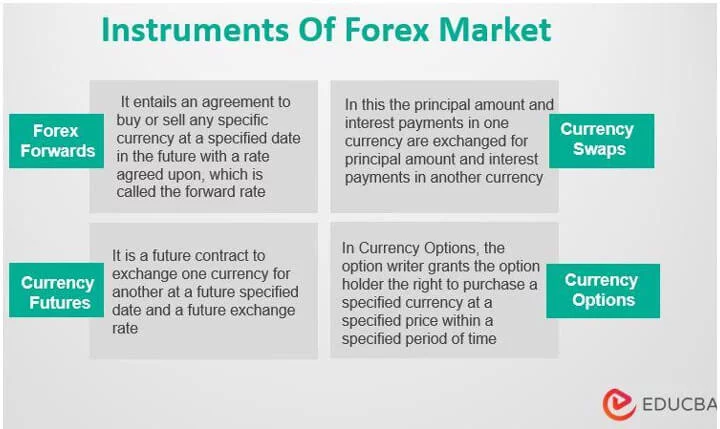
3. Forward Market
In contrast to the spot market, the forward market involves the sale or purchase of currencies for future delivery. The exchange rate is agreed upon at the time of the transaction, but the actual exchange occurs on a specified future date. Forward contracts are commonly used for hedging purposes.
4. Futures Market
The futures market involves standardized contracts to buy or sell a specific amount of currency on a future date. These contracts are traded on regulated exchanges and are subject to daily price fluctuations. Futures contracts are popular among institutional investors and speculators.
5. Options Market
Options give traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell currencies at a predetermined price within a specified period. Currency options provide flexibility and can be used to hedge against adverse price movements or speculate on future exchange rate movements.
Trading Dynamics in Forex:
Successful currency trading requires a profound understanding of various instruments and the factors influencing exchange rates. Traders leverage the following instruments and concepts:
Spot Market:
- The spot market involves the immediate exchange of currencies at the current market rate. This is the primary marketplace for Forex traders.
Forwards and Futures:
- Traders utilize forward and futures contracts to lock in future exchange rates, providing a hedge against currency fluctuations.
Options:
- Currency options grant the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency pair at a predetermined price before or at the option's expiry.
Leverage:
- Leverage allows traders to control a large position with a relatively small amount of capital. While it magnifies potential profits, it also increases the risk of significant losses.
Technical and Fundamental Analysis:
- Traders employ technical analysis by studying historical price charts and patterns, while fundamental analysis involves evaluating economic indicators, interest rates, and geopolitical events.
Risk Management and Caution:
Currency trading in Forex can be highly lucrative, but it comes with inherent risks. Traders must implement effective risk management strategies, including setting stop-loss orders and diversifying their portfolios. Additionally, staying informed about global economic events and market trends is crucial to making informed decisions.
Remember that currency trading involves significant risks, and it is advisable to seek professional advice or undergo proper training before engaging in live trading activities.
Currency trading in the Forex market is a captivating journey into the heart of global finance. Understanding the intricacies of currency pairs, utilizing various instruments, and implementing sound trading strategies are essential elements for success in this dynamic and ever-evolving realm. As with any financial endeavor, prudent risk management and continuous learning form the bedrock of a successful currency trading journey.

Leave a Reply